Contents

Batterry bulge is a common issue that occurs when batteries swell due to internal gas buildup from chemical reactions. This problem is particularly prevalent in lithium batteries, where factors such as overcharging, aging, and environmental stress can accelerate the swelling process. For example, volumetric expansion in the anode during charge cycles can result in fractures and restrict lithium-ion migration, ultimately reducing the battery’s capacity. Batteries that experience batterry bulge not only suffer from diminished performance but also present safety risks, making proper handling and timely replacement essential.
Key Takeaways
Charging too much or wrong voltage makes batteries swell. Use the right charger and unplug devices when fully charged.
Old batteries swell more because chemicals break down over time. Check and change old batteries often to stay safe.
Very hot or cold places can make batteries swell. Keep batteries in a cool, dry spot to avoid pressure and last longer.
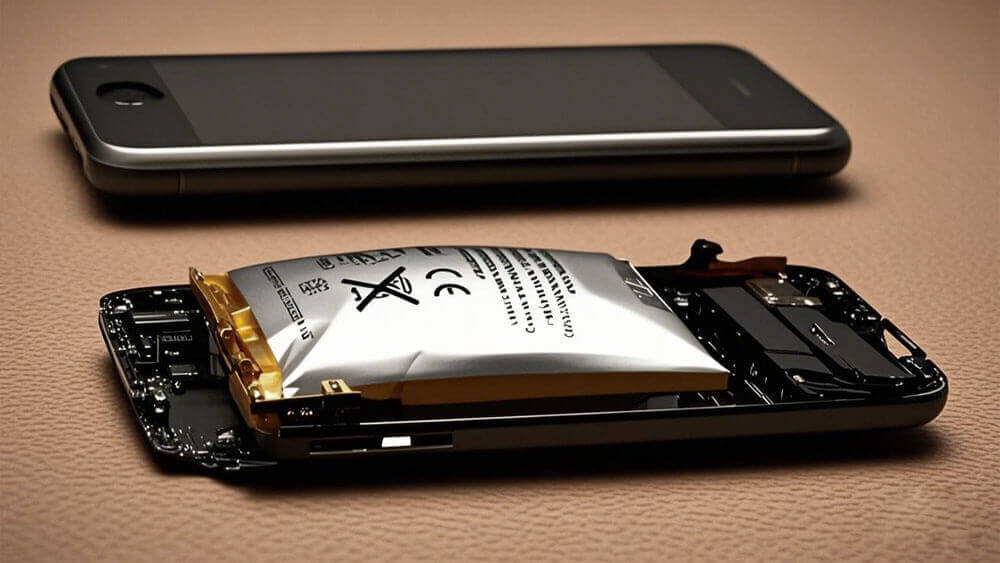

Part 1: Causes of Lithium Battery Swelling
1.1 Overcharging and Voltage Issues
Overcharging is one of the primary reasons why lithium batteries swell. When you overcharge a battery, it accelerates parasitic reactions between the electrodes and the electrolyte. These reactions generate heat and release gas, leading to internal pressure buildup. The electrochemical oxidation of electrolyte solvents on the cathode further exacerbates this issue, causing gassing and physical expansion.
Voltage irregularities also destabilize the chemical balance within the battery. For instance, exceeding the recommended voltage threshold can trigger thermal runaway, a condition where heat generation spirals out of control. This not only results in a swollen battery but also increases the risk of fire or explosion. To prevent such issues, you should always use chargers designed specifically for your battery type and avoid leaving devices plugged in for extended periods.
1.2 Aging and Chemical Degradation
As batteries age, their internal components degrade, making them more susceptible to swelling. Over time, repeated charge and discharge cycles cause the anode and cathode materials to deteriorate. This degradation restricts lithium-ion migration, leading to reduced capacity and efficiency. Additionally, the formation of a solid electrolyte interphase (SEI) layer on the anode can trap lithium ions, further diminishing performance.
Chemical degradation also contributes to gas generation within the battery. For example, the breakdown of electrolyte solvents releases gases that accumulate over time. Aging batteries are particularly prone to this issue, as their ability to contain and manage internal pressure weakens. Regular maintenance and timely replacement of old batteries can help you avoid the risks associated with aging and chemical degradation.
1.3 Environmental Factors and Temperature Extremes
Environmental conditions play a significant role in lithium battery swelling. Extreme temperatures, whether high or low, can negatively impact battery performance and longevity. Studies have shown that elevated temperatures accelerate chemical reactions within the battery, leading to increased gas generation and swelling. For instance, at discharge rates of 1 and 2 C, battery performance remains above 70% except at temperatures below -20°C and -30°C. However, at higher discharge rates, heat generation intensifies, further stressing the battery.
Cold environments also pose challenges. At temperatures below -20°C, the electrolyte’s viscosity increases, hindering ion flow and reducing efficiency. This can lead to uneven charge distribution and localized swelling. To mitigate these risks, you should store and operate batteries within the manufacturer-recommended temperature range. Proper insulation and cooling mechanisms can also help maintain optimal performance in extreme conditions.
1.4 Manufacturing Defects and Quality Control
Manufacturing defects are another critical factor contributing to lithium battery swelling. Poor quality control during production can result in structural weaknesses or impurities within the battery. For example, computed tomography (CT) analysis of commercial e-cigarette and smartphone batteries has revealed defects such as uneven electrode coatings and contamination. These flaws can disrupt the chemical balance, leading to gas buildup and swelling.
Inconsistent assembly processes also increase the likelihood of a bulging battery. Misaligned components or inadequate sealing can compromise the battery’s ability to contain internal pressure. To ensure safety and reliability, you should choose batteries from reputable manufacturers with stringent quality control measures. Investing in high-quality batteries reduces the risk of swelling and extends the lifespan of your devices.
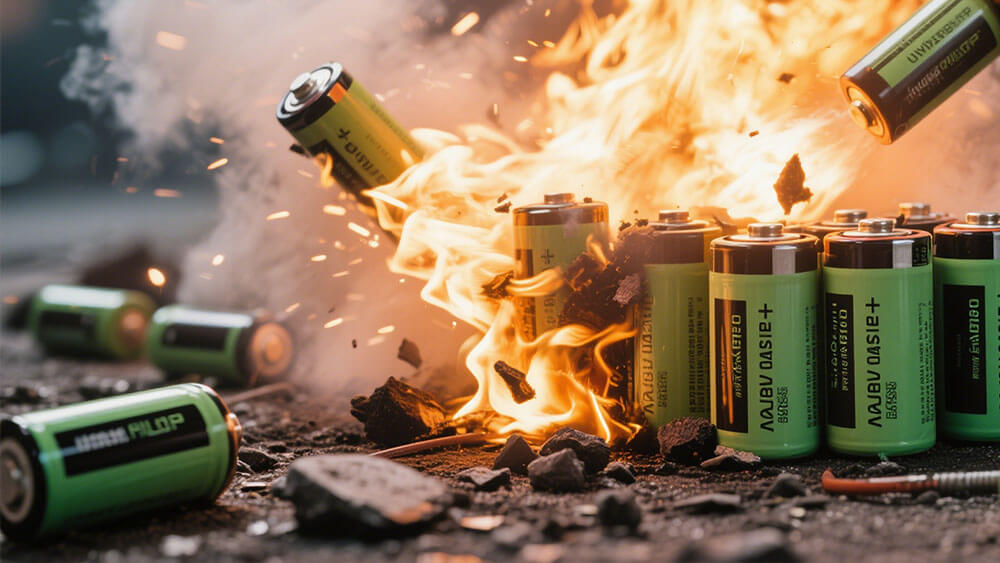

Part 2: Risks of a Swollen Battery
2.1 Fire and Explosion Hazards
A swollen battery poses a significant fire and explosion risk. When internal pressure builds up due to gas generation, the battery casing may rupture, exposing flammable materials to oxygen. This can lead to thermal runaway, a chain reaction that generates intense heat and ignites the battery. Lithium-ion batteries are particularly vulnerable to this phenomenon because of their high energy density.
Real-world incidents highlight the dangers of swollen batteries. For example:
On August 27, 2017, a Dell laptop user reported battery swelling that distorted the laptop casing.
On July 25, 2017, a portable MP3 player experienced a spontaneous lithium-ion battery fire, causing smoke and device damage.
On April 9, 2017, a Kobo Arc tablet emitted smoke after being fully charged, filling the room with hazardous fumes.
These cases underscore why lithium battery swelling should never be ignored. To minimize risks, you should immediately replace any swollen battery and avoid using damaged devices. Proper charging practices and regular inspections can also help prevent such hazards.
2.2 Damage to Devices and Equipment
Swollen batteries can cause irreversible damage to your devices. As the battery expands, it exerts pressure on the surrounding components, often leading to structural deformation. For instance, a swollen battery in a smartphone may push the screen outward, compromising its functionality and safety. Similarly, in laptops, battery swelling can warp the chassis, making the device unusable.
Statistics reveal the extent of this issue:
In 2021, Microsoft Surface Pro and Surface Book users reported 257 cases of damage caused by swollen batteries, including broken chassis and burned components.
An Apple iPhone 12 user experienced screen displacement due to battery swelling, rendering the device unsafe for use.
To protect your devices, you should monitor battery health regularly and store batteries in a cool, dry environment. Investing in high-quality batteries from reputable manufacturers can also reduce the likelihood of swelling and associated damage.
2.3 Environmental and Health Concerns
Swollen batteries not only threaten device safety but also pose environmental and health risks. When a battery swells and leaks, it releases harmful chemicals into the environment. These chemicals can contaminate soil and water, disrupting ecosystems and endangering wildlife. Improper disposal of swollen batteries exacerbates this problem, as landfills often lack the infrastructure to handle hazardous waste.
From a health perspective, exposure to battery chemicals can cause respiratory issues, skin irritation, and other medical complications. For example, inhaling fumes from a leaking battery can irritate your lungs and lead to long-term health problems. To mitigate these risks, you should dispose of swollen batteries responsibly by taking them to certified recycling centers. This not only protects the environment but also ensures compliance with safety regulations.
For more information on sustainable battery practices, visit Sustainability at Large Power.

Part 3: Identifying and Preventing Battery Swelling
3.1 Recognizing Signs of a Swollen Battery
Identifying early signs of battery swelling is crucial for preventing safety hazards. You should inspect your batteries regularly, especially before and after seasonal changes. Common indicators include physical deformation, such as bulging or warping of the battery casing, and difficulty fitting the battery into its designated compartment. Devices may also exhibit unusual behavior, like overheating or reduced performance.
Swollen batteries are not normal and signal underlying issues that could lead to dangerous situations, including leaks or explosions. Immediate replacement of a swollen battery is essential to avoid these risks. Regular inspections help you catch these signs early, ensuring the safety of your devices and environment.
3.2 Best Practices for Charging Lithium Batteries
Proper charging practices play a significant role in preventing lithium battery swelling. Always use chargers designed for your specific battery type to maintain voltage stability. Avoid overcharging by unplugging devices once they reach full capacity. Continuous charging can accelerate chemical reactions, leading to gas buildup and swelling.
You should also refrain from using fast chargers unless explicitly recommended by the manufacturer. While convenient, fast charging generates excess heat, which stresses the battery and increases the risk of swelling. Following these practices ensures optimal battery health and longevity.
3.3 Proper Storage and Handling Guidelines
Storing and handling batteries correctly minimizes the risk of swelling. Keep batteries in a cool, dry environment, away from direct sunlight or heat sources. Extreme temperatures can accelerate chemical reactions, causing internal pressure buildup.
When handling batteries, avoid puncturing or bending them, as physical damage can compromise their structural integrity. For long-term storage, maintain a charge level between 40% and 60% to prevent over-discharge or overcharge-related swelling. Proper storage and handling protect your batteries and extend their lifespan.
3.4 Regular Maintenance and Inspection Tips
Routine maintenance and inspections are vital for preventing lithium battery swelling. Check your batteries for physical damage, discoloration, or unusual odors. These signs often indicate internal issues that could lead to swelling.
You should also monitor battery performance, such as charge retention and discharge rates. Declining performance may signal aging or chemical degradation. Replace old or damaged batteries promptly to avoid safety risks. Regular maintenance ensures your batteries remain reliable and safe for use.
Lithium battery swelling results from internal gas buildup caused by overcharging, aging, and environmental stress. Degradation processes like SEI layer growth and lithium plating worsen under high temperatures, increasing swelling risks. Swollen batteries can lead to fires, device damage, and costly repairs. Always stop using the battery immediately and replace it to ensure safety.
Explore customized lithium battery solutions from Large Power.
FAQ
1. What should you do if your battery starts swelling?
Stop using the device immediately. Remove the battery if possible, and dispose of it at a certified recycling center to prevent safety hazards.
Tip: For professional guidance on battery starts swelling, visit Large Power.
2. Can you repair a swollen battery?
No, you cannot repair a swollen battery. Attempting to fix it increases the risk of fire or explosion. Always replace it with a new one.
3. How can you safely dispose of a swollen battery?
Take it to a certified e-waste recycling center.
Avoid puncturing or compressing the battery.
Never throw it in regular trash to prevent environmental harm.