Contents

LiPo batteries explode due to factors like thermal runaway, overcharging, or manufacturing flaws. Thermal runaway incidents have risen by 28% in aviation, highlighting the risks of hazardous gases in industrial applications. Overcharging or defective separators can also cause overheating. Prioritizing safety through proper handling and monitoring minimizes these dangers effectively.
Key Takeaways
- LiPo batteries can blow up from overheating, overcharging, or damage. Always check battery heat and avoid overcharging to stay safe.
- Check batteries often for swelling, leaks, or strange smells. Replace damaged batteries right away to avoid danger.
- Use the right chargers and keep batteries in fireproof boxes. Storing and handling them correctly lowers risks and makes them last longer.
- Routine inspectionsstely to ensure the safety of your equipment and personnel.
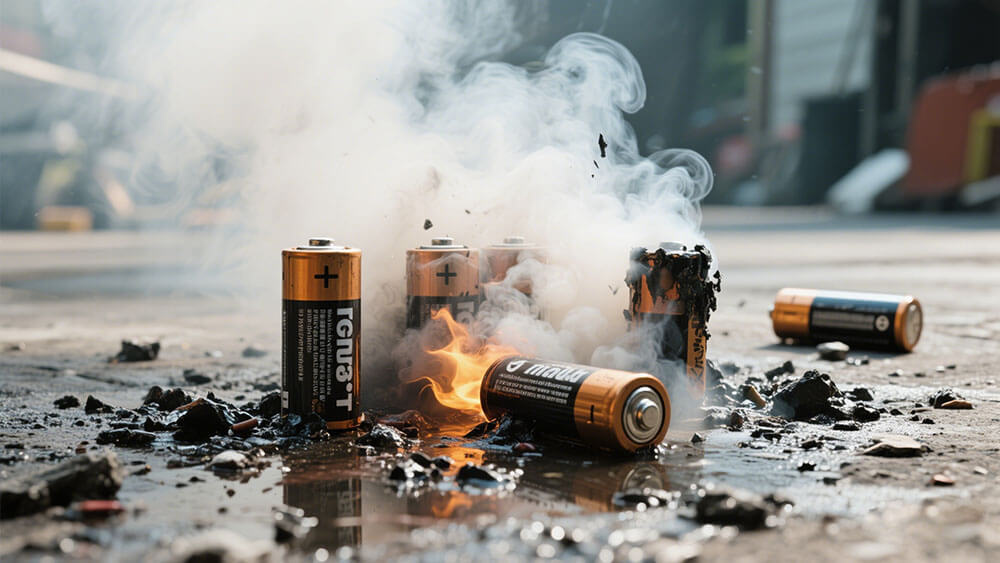

Part 1: Why Do LiPo Batteries Explode?
1.1 Thermal Runaway and Its Role in Lithium Battery Explosions
Thermal runaway is the primary cause of lithium battery explosions. It occurs when a battery’s internal temperature rises uncontrollably, triggering a chain reaction of heat generation. This process can lead to the release of flammable gases, which ignite under certain conditions. A study published in the journal FUEL highlights the dangers of thermal runaway. Researchers conducted 21 experiments simulating ignition scenarios in a controlled environment. They measured pressure rises and identified thresholds that could cause structural damage or injury. These findings emphasize the critical need to monitor battery temperatures during operation and charging.
1.2 Overcharging and Voltage Imbalance in Battery Packs
Overcharging is another significant factor that can cause lithium-ion batteries to explode. When a battery is charged beyond its voltage limit, it destabilizes the internal components. This can lead to overheating and the release of volatile electrolytes. These electrolytes produce flammable gases when exposed to high temperatures, increasing the risk of explosion. Additionally, voltage imbalances in battery packs exacerbate this issue. Uneven charging causes the battery to explode in extreme cases. To mitigate these risks, you should use chargers compatible with the battery’s specifications and implement battery management systems (BMS) to regulate voltage levels.
1.3 Physical Damage and Its Impact on Battery Safety
Physical damage to lithium batteries significantly increases the likelihood of thermal runaway. Dropping or puncturing a battery can cause internal short circuits, leading to rapid temperature spikes. Studies show that damaged batteries can release enough gas during thermal runaway to harm structures and individuals. For instance, a punctured battery may experience localized heating, which can escalate into a full-scale explosion. To prevent such incidents, you should handle battery packs with care and inspect them regularly for signs of wear or damage.
1.4 Manufacturing Defects and Quality Control Issues
Manufacturing defects also contribute to lithium battery explosions. Flaws such as damaged separators or the presence of metallic impurities can lead to internal short circuits. These defects often go unnoticed during production but manifest during charging or operation. Poor quality control exacerbates this problem, especially in large-scale battery packs. Choosing reputable manufacturers and ensuring rigorous quality checks can minimize the risk of explosions caused by defective batteries.

Part 2: Warning Signs of a Failing LiPo Battery
2.1 Swelling or Bulging in Battery Packs
Swelling or bulging is one of the most common warning signs of a failing lithium battery. This condition occurs due to gas accumulation caused by internal chemical reactions. A swollen battery indicates severe internal damage and poses a significant safety risk. You should replace any battery showing these signs immediately to avoid potential hazards. Ignoring this issue can lead to overheating, leakage, or even thermal runaway. Regularly inspecting battery packs for physical deformities ensures early detection of such problems.
2.2 Overheating During Operation or Charging
Overheating is another critical indicator of a failing lithium battery. It often arises during charging or operation and can escalate into dangerous situations. Several factors contribute to overheating, including rapid charging, overcharging, or using substandard chargers. These practices can create dendrites, which cause internal short circuits and excessive heat. Monitoring the charging process and employing balancing chargers designed for LiPo batteries can mitigate these risks. Additionally, avoid charging batteries in hot environments, as this exacerbates overheating and increases the likelihood of failure.
2.3 Leaks, Smoke, or Unusual Odors from Batteries
Leaks, smoke, or unusual odors are unmistakable signs of a failing lithium battery. These symptoms often indicate electrolyte leakage or internal combustion. If you notice any of these warning signs, disconnect the battery immediately and move it to a safe location. Leaking electrolytes are highly flammable and can ignite when exposed to heat or sparks. Proper handling and storage of batteries reduce the chances of such incidents. Always use fireproof containers for storing damaged or suspect battery packs.
2.4 Rapid Voltage Drops and Performance Issues
Rapid voltage drops and declining performance are common warning signs of a failing lithium battery. These issues typically result from internal degradation or imbalances within the battery pack. A failing battery may struggle to hold a charge, leading to inconsistent performance. You can use a battery management system (BMS) to monitor voltage levels and detect irregularities early. Addressing these problems promptly prevents further damage and ensures the safe operation of your battery packs.

Part 3: Practical Tips for Safely Using Lithium Batteries
3.1 Use Compatible Chargers and Avoid Overcharging
Using the correct charger is essential to prevent the overcharging of the battery cell. Chargers designed specifically for lithium batteries include built-in safeguards that regulate voltage and current. These features protect the battery from overheating and swelling, which can lead to thermal runaway.
Overcharging: Charging a LiPo battery beyond its recommended voltage can cause it to overheat, swell, and potentially enter thermal runaway. This is why it’s critical to use chargers specifically designed for LiPo batteries, with built-in safeguards to prevent overcharging.
To avoid overcharging and overdischarging, always monitor the charging process and disconnect the charger once the battery reaches full capacity. This simple step ensures safety and prolongs battery life.
3.2 Store Batteries in Fireproof Containers and Cool Environments
Proper storage is crucial for lithium battery safety. Always store batteries in fireproof containers to minimize the risk of fire in case of thermal runaway. Keep devices cool by placing them in environments with stable temperatures, away from direct sunlight or heat sources. High temperatures accelerate battery aging and increase the likelihood of failure. Fireproof storage solutions provide an additional layer of protection, especially for industrial battery packs.
3.3 Regularly Inspect Battery Packs for Damage or Wear
Inspecting battery packs regularly helps you identify potential issues before they escalate. Look for signs of swelling, leaks, or physical damage. Damaged batteries are more prone to short circuits, which can lead to overheating or fire. Replace any compromised battery immedia are a simple yet effective way to protect from physical damage and maintain operational efficiency.
3.4 Avoid Extreme Temperatures and Mechanical Stress
Extreme temperatures and mechanical stress significantly impact battery performance and longevity. High temperatures reduce capacity, increase internal resistance, and accelerate aging. Mechanical stress, such as dropping or puncturing a battery, can cause internal short circuits, leading to thermal runaway.
- High temperatures can lead to decreased capacity, meaning the battery holds less charge.
- Increased internal resistance due to heat results in lower power output and efficiency.
- Exposure to high temperatures accelerates aging, leading to quicker degradation of battery components.
- There is a heightened risk of thermal runaway when batteries are subjected to excessive heat.
Avoid exposing batteries to harsh conditions to ensure their reliability and safety.
3.5 Implement Battery Management Systems (BMS) for Monitoring
Battery management systems (BMS) play a vital role in monitoring battery health and ensuring safe operation. These systems track voltage, current, and temperature to prevent catastrophic events like fires or explosions. They also balance individual cells within a battery pack, extending its lifespan and maintaining optimal performance.
| Functionality | Description |
|---|---|
| Voltage, Current, and Temperature | Control and measurement of battery parameters to ensure safe operation. |
| SOC and SOH assessment | Evaluation of State of Charge and State of Health for effective battery management. |
| Detection of fault | Identifying issues within the battery system to prevent failures. |
| Passive cell balancing | Ensuring all cells in a battery pack are charged evenly to prolong battery life. |
| Data storage | Keeping records of battery performance for analysis and future reference. |
By implementing a BMS, you can monitor battery health effectively and reduce the risk of failure.

Part 4: How to Minimize the Risk of Lithium Battery Explosions
4.1 Choose Reputable Manufacturers for Battery Packs
Selecting a reliable manufacturer is crucial to minimize the risk of lithium battery explosions. Reputable manufacturers adhere to stringent quality standards, ensuring their battery packs meet safety and performance benchmarks. Certifications like ISO, UL, and CE validate a manufacturer’s commitment to quality and safety. For instance:
| Certification | Description |
|---|---|
| ISO | Indicates adherence to quality management standards. |
| UL | Ensures safety and performance standards are met. |
| CE | Confirms compliance with health, safety, and environmental protection standards. |
| RoHS | Restricts hazardous substances in electrical and electronic equipment. |
| ISO 14001 | Focuses on effective environmental management systems. |
| UN 38.3 | Certifies safe transport of lithium batteries. |
When sourcing battery packs, prioritize manufacturers with these certifications. This reduces the risk of explosion caused by manufacturing defects or substandard materials.
4.2 Dispose of Damaged or Aged Batteries Responsibly
Damaged or aging batteries pose significant risks, including thermal runaway and fire hazards. You should replace aging batteries promptly and dispose of them responsibly. Improper disposal can lead to environmental contamination and increase the risk of explosion during waste processing. Use certified recycling facilities that comply with environmental regulations. These facilities safely handle hazardous materials, ensuring minimal environmental impact. Always store damaged batteries in fireproof containers until you can dispose of them properly.
4.3 Establish Safety Protocols for Storage and Transport
Proper storage and transport protocols are essential to minimize risks. Store lithium batteries in cool, dry environments away from flammable materials. Use fireproof containers to contain potential thermal runaway incidents. During transport, secure battery packs to prevent physical damage or short circuits. Adhering to guidelines like UN 38.3 ensures safe handling during shipping. Implementing these safety measures reduces the likelihood of accidents and protects personnel and property.
Tip: Regularly train your team on storage and transport protocols to ensure compliance and enhance workplace safety.
LiPo batteries explode due to thermal runaway, overcharging, and physical damage. You can mitigate these risks by prioritizing safety through proper handling, regular inspections, and using high-quality battery packs. Implementing best practices ensures reliable performance and reduces hazards, enabling the safe use of lithium batteries in industrial and commercial environments.
FAQ
1 How can you safely transport LiPo battery packs?
Use fireproof containers and secure the batteries to prevent movement. Follow UN 38.3 guidelines for safe transport. Train your team on proper handling procedures.
Tip: Label battery shipments clearly to comply with international safety standards.
2 What should you do if a LiPo battery starts swelling?
Immediately stop using the battery and place it in a fireproof container. Dispose of it responsibly at a certified recycling facility to avoid safety hazards.
3 Can you repair a damaged LiPo battery pack?
No, repairing damaged LiPo batteries is unsafe. Internal damage increases the risk of thermal runaway. Replace the battery with a new one from a reputable manufacturer.
Note: Attempting repairs can void warranties and compromise safety.